Laboratory Testing Strategies by WHO for COVID-19
Covid-19 Antigen Test
Have Any Questions?
If you have any query or looking for the best medical laboratory then Bio Covid Lab is always there. feel free to Contact.
What is COVID-19?
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). COVID-19 was identified in December 2019 and declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization in March 2020.
Type and severity of symptoms of an active COVID-19 infection vary greatly between individuals depending on the age, gender, and underlying medical conditions. The most commonly reported ones include fever, loss of smell, coughing, sore throat, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling weak or lethargic, chills, muscle pain, light-headedness or dizziness, headache, vomiting or diarrhea, slurred speech, and/or seizures. Less common symptoms include stuffy nose, conjunctivitis (pink eye), dizziness, confusion, abdominal pain, and skin rashes or discoloration of fingers or toes.
Type and severity of symptoms of an active COVID-19 infection vary greatly between individuals depending on the age, gender, and underlying medical conditions. The most commonly reported ones include fever, loss of smell, coughing, sore throat, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling weak or lethargic, chills, muscle pain, light-headedness or dizziness, headache, vomiting or diarrhea, slurred speech, and/or seizures. Less common symptoms include stuffy nose, conjunctivitis (pink eye), dizziness, confusion, abdominal pain, and skin rashes or discoloration of fingers or toes.
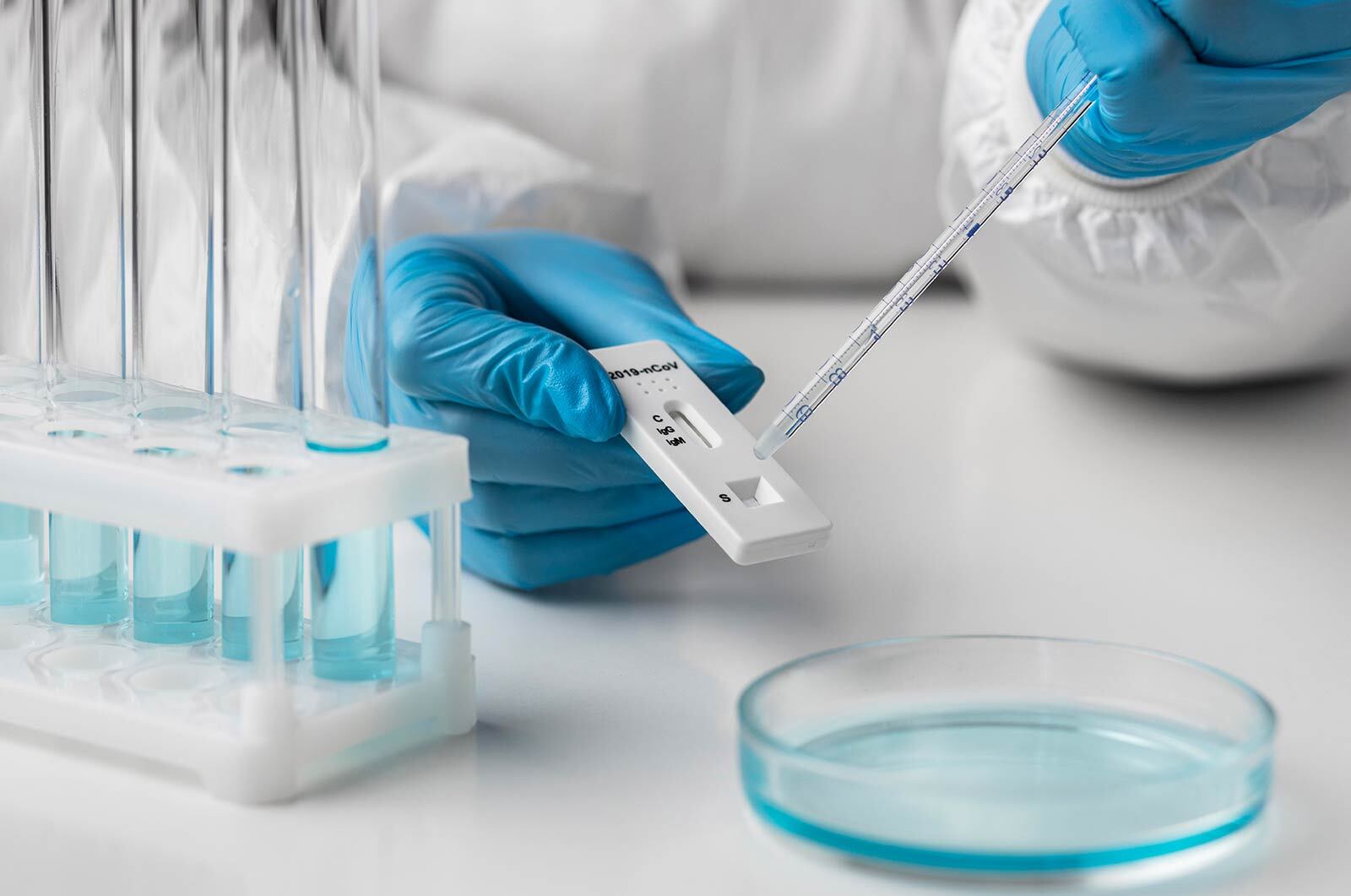

Antigen Test
Until now, the majority of rapid diagnostic tests have been antigen tests. They are taken with a nasal or throat swab and detect a protein that is part of the coronavirus. These tests are particularly useful for identifying a person who is at or near peak infection. Antigen tests are less expensive and generally faster.
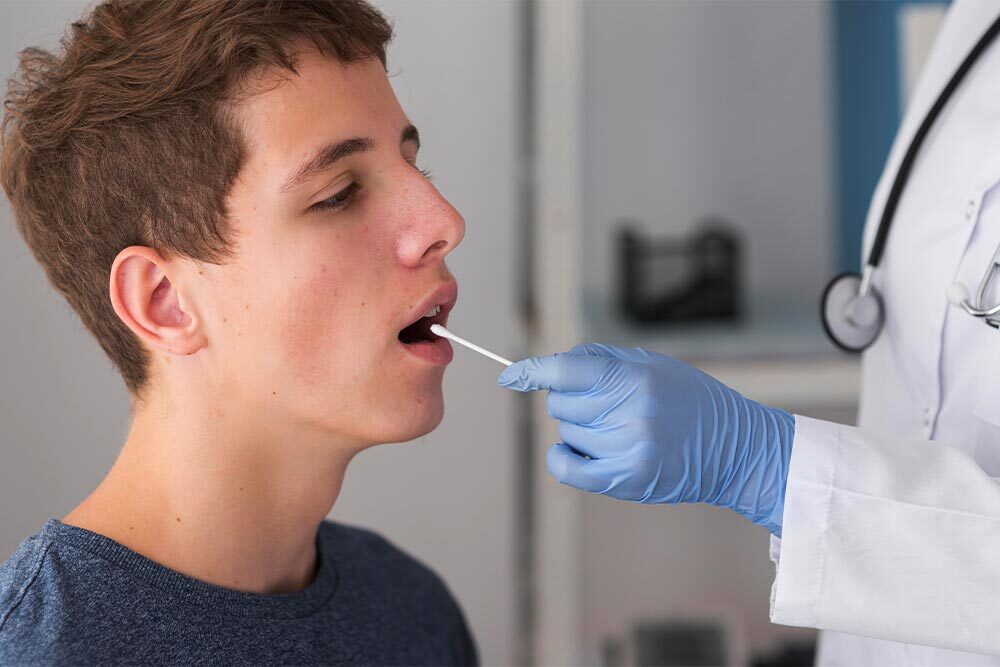
Procedure Of Rapid Antigen Test
Specimen: Nasopharyngeal swab
What the test will look for: Antigen (Protein) of Covid-19 Virus.
Process: Nasal samples are collected and tested for antigens, which are found in the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It can be even performed outside the conventional laboratory setting. This test is used to quickly obtain a diagnostic result. This test is a rapid chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection of specific antigens to SARS-CoV-2 present in the human nasopharynx. It provides only an initial screening test result. More specific alternative diagnosis methods should be performed in order to obtain the confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 an infection like COVID 19 PCR.
What the test will look for: Antigen (Protein) of Covid-19 Virus.
Process: Nasal samples are collected and tested for antigens, which are found in the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It can be even performed outside the conventional laboratory setting. This test is used to quickly obtain a diagnostic result. This test is a rapid chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection of specific antigens to SARS-CoV-2 present in the human nasopharynx. It provides only an initial screening test result. More specific alternative diagnosis methods should be performed in order to obtain the confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 an infection like COVID 19 PCR.
Difference Between a COVID-19 Antigen and PCR Test?
- An antigen test checks the presence of a specific viral antigen, which implies current viral infection. Rapid antigen tests may show results in about 15 minutes.
- PCR tests check for genetic material (viral RNA) produced by the virus. It determines if you’re currently infected and can spread COVID-19 to others.
- Antigen tests have lower sensitivity than PCR tests, which may result in a higher false negative rate.
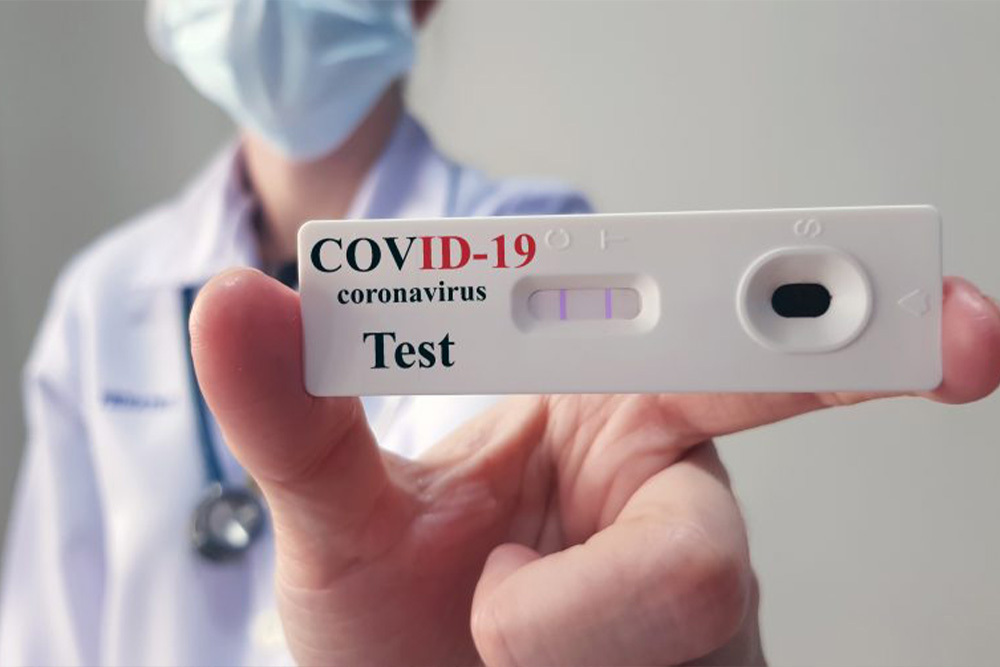
What will my COVID-19 Antigen Test results tell me?
Your test results may imply that you are currently infected with COVID-19, but your results will need to be confirmed by a COVID-19 PCR test. If your results are positive, it is important to isolate immediately and continue to monitor your symptoms. If your results are negative, this may suggest the virus was not present in the sample you provided. However, if you’re having symptoms of COVID-19, you may need to be tested with a COVID-19 PCR test.
